3 Core Cable, what is it used for vs 2 Core Cable? - Electrical Faults Fixed
Table of Contents
- 3 core cable, what is it used for vs 2 core cable
- Understanding Cable Basics
- What is a 3-core cable?
- What is a 2-core cable?
- Uses of 3-core cables
- Uses of 2-core cables
- Comparing 3-core and 2-core cables
- Choosing between 3-core and 2-core cables
- Cable quality and standards
- Advanced cable types
- Conclusion
1) 3 core cable, what is it used for vs 2 core cable
As a fully qualified electrician with years of experience in various electrical projects and installations, I've worked extensively with different types of cables. Today, I want to share my knowledge about 3-core and 2-core cables, explaining what they are, their uses, and how they compare. This information is for anyone involved in electrical work or wanting to understand more about electrics from DIY enthusiasts to professional contractors.
Back to top2) Understanding Cable Basics
Before we get into the specifics of 3-core and 2-core cables, let's cover some basics. An electrical cable typically consists of one or more conductors (usually copper wires) covered by non-conductive material for insulation and protection. The number of cores in a cable refers to the number of separate wires within the outer sheath. Most fixed wiring is manufactured in solid cores in a circular shape. The cable as a whole is either flat (common for residential use) or circular and contains different components.
Back to top3) What is a 3-core cable?
A 3-core cable, also known as a three-core cable or 3-wire cable, contains three separate wires within a single outer sheath. Each wire is individually insulated and color-coded for easy identification. In a standard 3-core cable, you'll typically find:
- A brown wire (live wire)
- A blue wire (neutral wire)
- A green/yellow wire (earth cable)
The live wire carries the electrical current from the power source to the device, the neutral wire completes the circuit by carrying the current back, and the earth wire provides a safety path to ground in case of a fault.
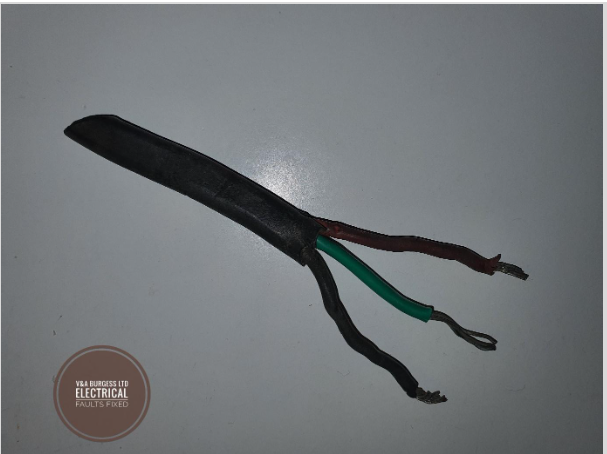

4) What is a 2-core cable?
In contrast, a 2-core cable, or two-core cable, contains only two wires within its outer sheath. These are typically:
- A brown wire (live wire)
- A blue wire (neutral wire)
Two-core cables don't include an earth wire, which limits their applications compared to 3-core cables. Multi core cables can contain 4,5 or more inner cores and have various purposes.
Back to top5) Uses of 3-core cables
3-core cables are incredibly versatile and are used in a wide range of electrical installations. Here are some common applications:
- Domestic appliances: Many household appliances that require an earth connection use 3-core cables. This includes washing machines, dishwashers, and electric ovens.
- Lighting circuits: In commercial buildings and some residential settings, 3-core cables are used for lighting circuits where earthing is required. The earth is often bare copper which is then sleeved by the electrician.
- Industrial applications: 3-core cables are often used in factories and other industrial settings for powering heavy machinery and equipment.
- Outdoor electrical applications: Due to their robust nature, 3-core cables are suitable for external electrical applications where protection against the elements is crucial.
- Three-phase power systems: In industrial and some commercial settings, 3-core cables are used for three-phase power distribution, where each core carries one of the three phases. Three-wire cables will only be acceptable where no neutral core or earth core is required in these applications. A fourth conductor is required where a neutral conductor is needed or a 5-core electrical cable where an earth or ground is needed.
6) Uses of 2-core cables
While 2-core cables have more limited applications due to the lack of an earth wire, they still have several important uses:
- Lighting circuits: In situations where earth conductors are not required, such as for Class II (does not require a ground connection) double-insulated light fittings, 2-core cables are often used. The fixed cables will often contain 3 cores (including the earth or ground) but cables inside Class II light fixtures will contain just two cores.
- Low voltage applications: Many low voltage devices and systems, such as doorbells or central heating systems, use 2-core cables.
Speaker systems: 2-core cables are commonly used for connecting speakers, where one core carries the positive signal and the other the negative. - Some small appliances: Certain double-insulated appliances andf electrical equipment that don't require an earth connection may use 2-core cables. The body of the equipment is normally not able to become live under fault conditions and therefore the manufacturer will certify it as Class II.
7) Comparing 3-core and 2-core cables
Now that we understand what these cables are and their typical uses, let's compare them directly:
- Safety: 3-core cables are generally considered safer for most applications due to the inclusion of an earth wire. This provides an additional layer of protection against electric shock in case of a fault.
- Versatility: 3-core cables are more versatile and can be used in a wider range of applications, especially where earthing is required.
- Cost: 2-core cables are usually less expensive due to having one less conductor and less material overall.
- Size: 2-core cables are typically smaller in diameter, which can be advantageous in tight spaces or when aesthetics is a concern.
- Regulatory compliance: In many jurisdictions, electrical codes require the use of earthed (3-core) cables for most household and commercial wiring. Always check your local electrical code for specific requirements.
8) Choosing between 3-core and 2-core cables
When deciding between a 3-core and a 2-core cable, consider the following:
- Application: What is the cable being used for? Does the device or circuit require an earth connection?
- Safety requirements: Is earthing necessary for the safety of the installation?
- Local regulations: What do your local electrical codes specify for the particular application?
- Future-proofing: Even if a 2-core cable meets current needs, consider whether future changes might require an earth connection.
- Environmental factors: Will the cable be exposed to harsh conditions that might necessitate the extra protection of a 3-core cable?
9) Cable quality and standards
Regardless of whether you're using 3-core or 2-core cables, high-quality cables that meet relevant standards should be used and purchased from reputable electrical wholesalers. Look for cables with proper certifications and those made by reputable manufacturers. Using substandard cables can lead to poor performance, increased risk of electrical fires, and potential legal issues if they don't meet local codes. The standard of the manufacturing process will have an impact on the lifespan of the cables.
Back to top10) Advanced cable types
While we've focused on basic 3-core and 2-core cables, it's worth mentioning that there are more complex cable types for specialized applications:
- Multi-core cables: These can have four, five, or even more cores for complex control systems or three-phase power with neutral and earth.
- Armored cables: Such as Steel Wire Armored (SWA) cables, which provide greater mechanical protection for underground or exposed runs. Multi core swa cable is common in industrial applications.
- Shielded cables: These include additional shielding to protect against electromagnetic interference, often used in sensitive electronic applications.
11) Conclusion
Understanding the differences between 3-core and 2-core cables is crucial for anyone involved in electrical work. While 3-core cables offer greater versatility and safety features, 2-core cables have their place in specific applications. Always consider the requirements of your project, local regulations, and safety standards when choosing between these cable types.
Remember, working with electricity can be dangerous. If you're unsure about which type of cable to use or how to install it correctly, it's always best to consult with or hire a qualified electrician. Safety should always be your top priority in any electrical project.
By choosing the right cable for your specific application, you can ensure the efficiency, safety, and longevity of your electrical installations. Whether you're wiring a new home, upgrading an industrial facility, or just replacing a simple appliance cord, the choice between 3-core and 2-core cables can make a significant difference in the success of your project.
Read more articles
- Log in to post comments