What is a Neutral wire in electrical wiring? - Electrical Faults Fixed
Table of Contents
- What is a Neutral Wire in Electrical Wiring?
- What is the Role of the Neutral Wire
- Neutral Wire Color Codes from USA to UK
- The Difference Between Neutral, Ground, and Hot (Line) Wires
- The Neutral Wire in Three-Phase Systems
- Common Problems with Neutral Wires
- Grounding / Earthing and the Main Service Panel
- Neutral Wires in Residential and Commercial Buildings
- Potential Hazards and the Need for Proper Installation
- Neutral Wires and Modern Electrical Systems
- Key Tips for Electrical Safety
- Conclusion
1) What is a Neutral Wire in Electrical Wiring?
The neutral wire serves a vital role in electrical systems, acting as a return path for the flow of electric current. It ensures the safe and efficient operation of electrical devices in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
This article explores the pivotal role of the neutral wire, its identification through color codes, and its relationship to the ground wire, hot wire, and live wire. We will also discuss potential hazards, its use in modern electrical systems, and proper installation in adherence to safety standards like the National Electrical Code (NEC) and BS7671 Wiring Regulations.
Back to top2) What is the Role of the Neutral Wire
The neutral electrical wire is an indispensable component of AC (alternating current) electrical systems. Its primary function is to provide a low-resistance path that completes the electrical circuit, allowing current flow back to the power source. In a standard AC system, the live conductor delivers power to an electrical load, while the neutral wire ensures the current back to the source.
This low resistance return path maintains the energy efficiency of the circuit and minimizes electrical hazards, such as fire hazards and electrical shock.
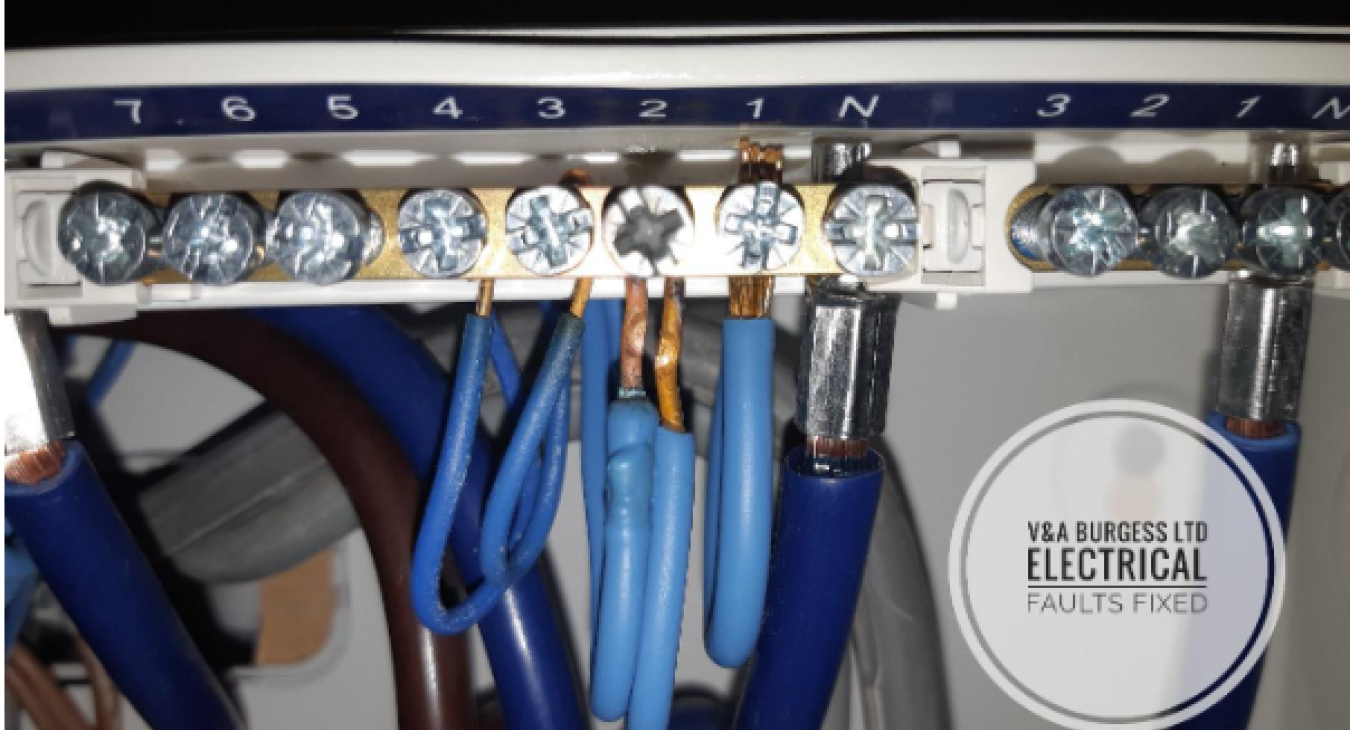
3) Neutral Wire Color Codes from USA to UK
The color codes used to identify the neutral wire vary by region:
- United States: The neutral wire is typically a white wire or gray in modern residential wiring.
- United Kingdom: The neutral wire is commonly identified by a blue color under current standards. In older houses, black was used as the neutral wire.
Correctly identifying the neutral wire is vital for proper installation, reducing the risk of electrical accidents and ensuring compliance with local electrical codes. In some cases, it may not be clear which wire is the neutral wire. In these cases, an electrician may be needed to correctly identify the wire using electrical test equipment.
Back to top4) The Difference Between Neutral, Ground, and Hot (Line) Wires
Electrical systems include three primary types of wires:
- Hot wire: Also called the line wire in the UK, carries high voltage from the power source to the load.
- Neutral wire: Completes the circuit by providing a return path for the electric current.
- Ground wire: Also called the Earth Wire in the UK. A safety wire that directs excess electricity from fault currents to the earth, preventing damage to electrical devices and reducing the risk of electric shock.
The neutral wire works closely with the ground wire as a safety feature, but they perform different functions. While the neutral wire carries current under normal conditions, the ground wire only becomes active during electrical faults.

(PHOTO: Old UK colored neutral in black, hot(line) conductor is red and grounding / earthing is yellow / green mix)
5) The Neutral Wire in Three-Phase Systems
In three-phase systems, the neutral wire serves as a reference point for balancing loads. When loads are balanced across the phases, the neutral carries minimal or zero current. However, if loads are unbalanced, the neutral provides a path for the difference in currents.
Balanced systems reduce any hazards, such as equipment damage and overheating. Proper installation by a licensed electrician is essential in such systems, especially in commercial buildings where three-phase power is common and used in the likes of motors and heating equipment.
Back to top6) Common Problems with Neutral Wires
Neutral wires are prone to several issues, including:
- Loose Connections: A loose neutral can result in voltage fluctuations, causing damage to electrical appliances or even fires if the resistance and heat build up.
- Short Circuits: Faulty wiring can lead to a short circuit, posing significant fire hazards and risking electrical shock.
- Old or Damaged Wiring: In older homes, aging wiring may compromise the safety of electrical systems.
These issues underscore the importance of hiring a qualified electrician to inspect and maintain electrical installations. A regular inspection by a professional can highlight common electrical problems that may go unnoticed otherwise.
Back to top7) Grounding / Earthing and the Main Service Panel
The neutral wire connects to the grounding wire or earthing wire at the main service panel, establishing a shared reference point. This connection provides a low-resistance path for fault currents, minimizing the risk of electrical hazards and ensuring the safety of electrical systems.
A properly installed ground rod / earth rod enhances this system by directing excess electricity safely into the earth. Following local electrical codes is critical to ensure the effectiveness of these safety measures.
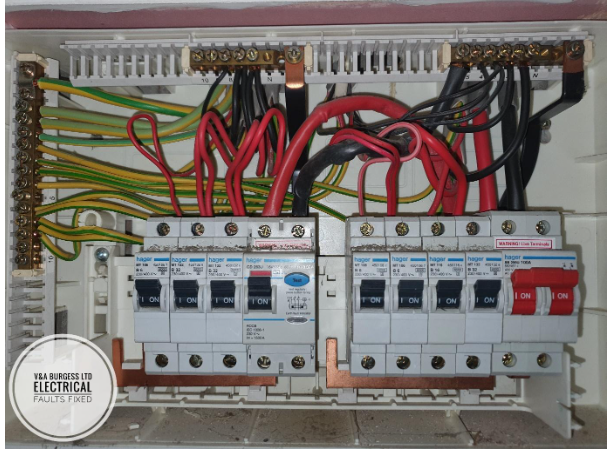
(PHOTO: A UK Electrical Panel / Consumer unit / Fuse Box)
Back to top8) Neutral Wires in Residential and Commercial Buildings
In residential settings, the neutral wire is a vital part of circuits powering outlets, light fixtures, and smart switches. In commercial buildings, the higher complexity of systems, often involving three-phase power, makes the neutral wire's pivotal role even more significant.
Whether in homes or businesses, the neutral wire ensures the seamless operation of the vast majority of electrical systems, preventing electrical faults and maintaining stability.
Back to top9) Potential Hazards and the Need for Proper Installation
Improper handling of neutral wires can result in several potential hazards, including:
- Electrical shock: Touching a live or loose neutral can result in serious injuries.
- Fire hazards: Faulty connections can spark fires, especially in older houses with outdated wiring.
- Equipment damage: Surges caused by neutral issues can harm sensitive electronics.
To avoid these risks, ensure the proper installation of all wiring and hire a licensed electrician for electrical work. Despite its name, the neutral wire is actually a LIVE CONDUCTOR and can carry voltages almost as high as the line conductor under certain circumstances. If a neutral wire is disconnected but the line conductor remains connected, the neutral will have the full mains voltage sat waiting.

(PHOTO: Multifunction tested can check for voltage, resistance and other electrical testing)
Back to top10) Neutral Wires and Modern Electrical Systems
In modern electrical systems, the neutral wire integrates seamlessly with innovations like solar power systems and advanced safety technologies. Devices such as three-prong plugs utilize the neutral and grounding wire to maximize safety and prevent equipment damage.
Back to top11) Key Tips for Electrical Safety
- Always identify the standard color of wires before working.
- Refer to the fine print in local electrical codes to ensure compliance.
- Ensure that the metal parts of electrical devices are properly grounded.
- Regularly inspect older wiring for potential hazards.
- Use circuit breakers and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) (or RCDs) for added protection against electrical hazards.
12) Conclusion
The neutral wire is an indispensable component of any electrical system, ensuring a safe and reliable, low resistance return path for electrical current. From providing stability in three-phase systems to enhancing the safety of electrical systems in homes and businesses, its role is undeniable. By adhering to local electrical codes and prioritizing proper installation, the risk of fire hazards, electric shock, and equipment damage can be significantly reduced.
Always consult a qualified electrician for any concerns, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of all electrical installations.
Read more articles
- Log in to post comments