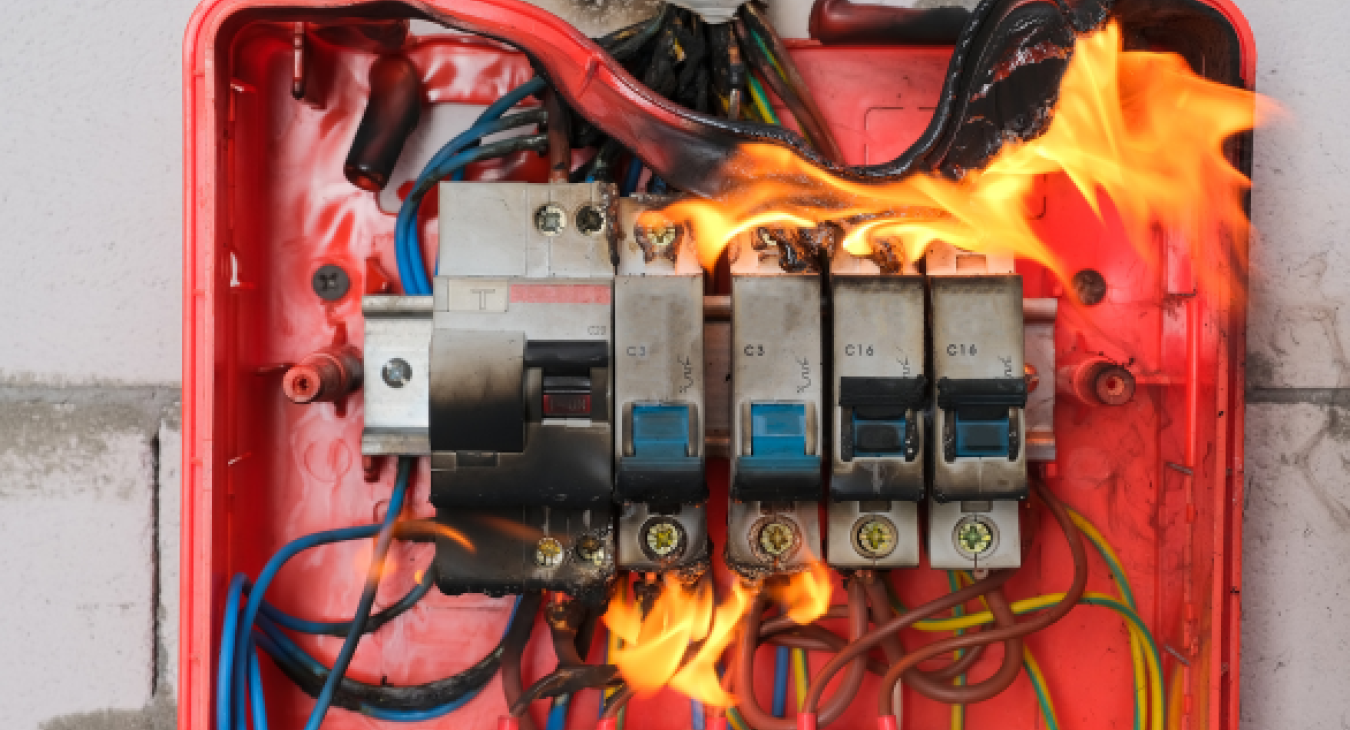
Electrical Short Circuit, definition and causes - Electrical Faults Fixed
Índice
- Cortocircuito eléctrico: definición y causas
- ¿Qué es un cortocircuito eléctrico?
- Partes de un circuito eléctrico
- Tipos de cortocircuitos eléctricos
- Causas comunes de los cortocircuitos
- Signs of a Short Circuit
- Preventative Measures and Safety Measures
- The Role of Circuit Breakers in Preventing Short Circuits
- Electrical Repair and Maintenance
- Summary
1) Cortocircuito eléctrico: definición y causas
Como electricista y profesor de electricidad, los clientes y estudiantes me preguntan con frecuencia sobre problemas eléctricos como: ¿Qué es un cortocircuito y por qué ocurren tales problemas?
Los cortocircuitos eléctricos se encuentran entre las causas más comunes de problemas eléctricos en hogares y propiedades comerciales. Comprender qué es un tiro eléctricoel circuito de rt, las causas potenciales y cómo prevenirlo son esenciales para garantizar la seguridad eléctrica. En este artículo, analizamos la definición de cortocircuito eléctrico, las causas comunes, los signos de daño y las medidas de seguridad que pueden ayudarlo a mantenerse seguro y a que su sistema eléctrico funcione correctamente.
Back to top2) ¿Qué es un cortocircuito eléctrico?
Se produce un cortocircuito eléctrico wcuando la corriente eléctrica fluye a lo largo de una ruta no deseada de conexión de baja resistencia en lugar de la ruta de circuito prevista. En condiciones de cortocircuito, el flujo de electricidad toma el camino de menor resistencia, lo que puede provocar un flujo de corriente excesivo y daños potenciales a los aparatos eléctricos, dispositivos y propiedades. Los cortocircuitos pueden causar altas temperaturas, a href="https://www.electricalfaultsfixed.com/blog/15-causes-electrical-fires-fire-safety-tips-2024"> incendios eléctricos y descargas eléctricas, por lo que requieren atención inmediata.
Back to top3) Partes de un circuito eléctrico
Para comprender cómo ocurre un cortocircuito, es importante conocer los componentes básicos de unacircuito:
- Cable con corriente (conductor de línea o cable caliente): transporta la energía eléctrica desde la fuente de alimentación (como el panel eléctrico) al equipo eléctrico.
- Cable neutro: completa el circuito llevando la corriente de vuelta a la fuente de alimentación.
- Conexión a tierra o cable de tierra: proporciona un camino seguro para que la electricidad fluya de regreso a tierra (tierra) en caso de una falla o falla a tierralt.

(Colores de cableado antiguos en un cable de goma antiguo)
En condiciones normales de funcionamiento, la corriente eléctrica fluye a lo largo de la línea (oCable CALIENTE), pasa a través de un aparato, bombilla u otro equipo eléctrico y regresa a través del conductor neutro. Un equipo eléctrico como este proporciona una impedancia o resistencia al flujo de corriente y minimiza el nivel al que puede elevarse la corriente eléctrica.
Cuando los conductores de corriente entran en contacto directo entre sí o con el cable de tierra, se produce un cortocircuitose genera, creando un peligro potencial.
Back to top4) Tipos de cortocircuitos eléctricos
Existen diferentes tipos de cortocircuitos, y cada tipo depende de la causa del cortocircuito y las conexiones eléctricas involucradas:
Cortocircuito normal: ocurre cuando un cable caliente entra en contacto con un cable neutro, lo que resulta en una trayectoria de baja resistencia que causa un flo de alta corrientew.
Fallo a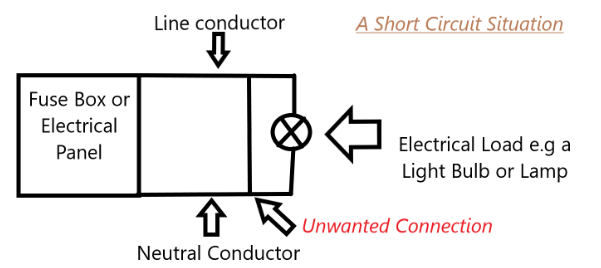
tierra: ocurre cuando un cable caliente toca un cable de tierra o un objeto metálico conectado al suelo, lo que lleva a una situación peligrosa en la que la electricidad sea través del cuerpo humano u otras vías conductoras.
Falla de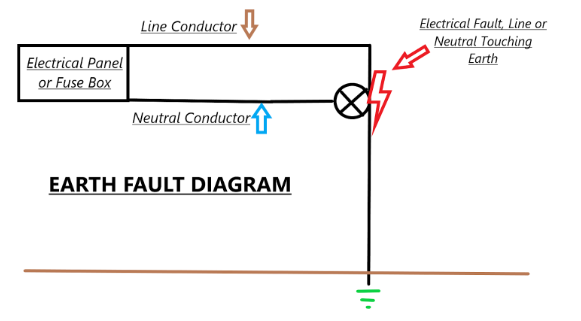
- arco: causada por cables dañados, conexiones de cables sueltos o aislamiento de cables rotos, lo que conduce a unaarco de calor que puede encender materiales inflamables cercanos. Los interruptores de circuito por falla de arco (AFCI o AFDD) están diseñados para detectar estas fallas y cortar la energía para evitar incendios eléctricos.
Back to top
5) Causas comunes de los cortocircuitos
Varios factores pueden causar un cortocircuito en el sistema eléctrico de una casa. A continuación se presentan las causas más comunes de cortocircuitos:
- Wir defectuosoing: Una de las principales razones de los cortocircuitos es un cableado defectuoso o problemas de cableado. Las conexiones eléctricas de mala calidad, las conexiones sueltas o el aislamiento dañado pueden provocar conexiones involuntarias entre los cables, creando una ruta de baja resistencia y un cortocircuito.
- Conexiones de cables sueltos: conexiones sueltas en componentes eléctricos, como en interruptores, salidasts, y los paneles de servicio, pueden provocar chispas y cortocircuitos. Las inspecciones eléctricas periódicas realizadas por un electricista con licencia pueden ayudar a detectar estos problemas a tiempo.
- Cableado defectuoso del electrodoméstico: los electrodomésticos y dispositivos eléctricos con cableado dañado o defectuoso del electrodoméstico pueden causar cortocircuitos. Esto puede suceder cuando los cables de alimentación o el cableado interno se deterioran o se convierten en EXPosed, lo que resulta en un contacto directo entre los cables.
Objetos metálicos: la inserción inadvertida de un objeto metálico, como un clavo o un tornillo, en una toma de corriente o en un cableado puede provocar un cortocircuito. El metal proporciona una ruta alternativa de baja resistencia, lo que resulta en un alto flujo de corriente.
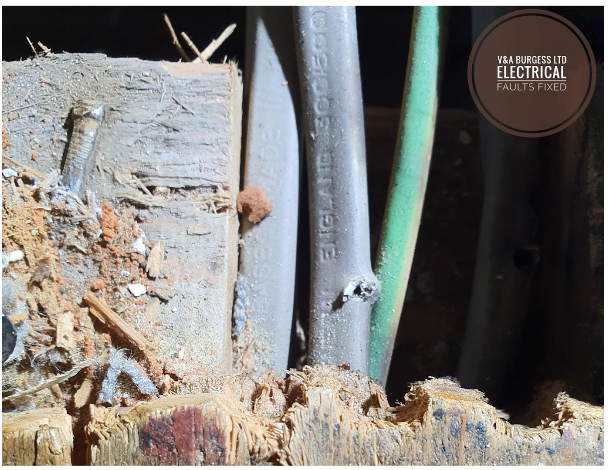

(Photo: Cables damaged under floorboards by screws)
- Water and Moisture: Water is a good conductor of electricity, and exposure to water or moisture can create a short circuit condition. This is especially common in areas like bathrooms and kitchens. GFCI outlets (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters) should be used in these areas to prevent electrical shocks.
6) Signs of a Short Circuit
Locating and fixing a short circuit is necessary for preventing considerable damage to the electrical system and possible property damage. Common signs of a short circuit are:
- Burn Marks: Scorch marks or burn marks around outlets or switches indicate a short circuit.
- Tripped Breaker: A circuit breaker that frequently trips is a sign of a short circuit. When the breaker trips, it prevents high current flow to protect the electrical system.
- Electrical Shock: A direct contact with an energized surface can lead to an electric shock, indicating a fault.
Unusual Odors or Sparks: Burning smells or visible sparks near outlets or wiring suggest a short circuit or another serious electrical fault.

7) Preventative Measures and Safety Measures
Prevention is the first step in avoiding electrical faults and ensuring electrical safety. Here are some preventative measures:
- Regular Electrical Inspections: Hire a licensed electrician to inspect the electrical panel (consumer unit, fuse box), wiring, and all electrical connections regularly to detect and fix potential hazards before they escalate. See electrical repair and maintenance below.
- Install AFCI and GFCI Outlets: Installing arc-fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) and GFCI outlets in key areas can help prevent electrical fires and electric shock by cutting off the power supply during faults.
- Repair Faulty Wiring and Appliances: If you notice any signs of damage, such as frayed power cords or faulty wiring, get them repaired immediately by a professional.
- Avoid Overloading Circuits: Do not overload outlets with too many electrical appliances or devices. Overloaded circuits can lead to overheating, high currents, and electrical fires.
- Keep Water Away from Electrical Equipment: Ensure that electrical devices are kept away from water sources. Use waterproof covers for outdoor outlets to protect against moisture.
8) The Role of Circuit Breakers in Preventing Short Circuits
Circuit breakers play a vital role in any home’s electrical system. They are designed to cut off power to a circuit if it detects an excessive current flow. When a breaker trips, it stops the flow of electricity, preventing further damage to the electrical components and the risk of fire. Tripped breakers are a common occurrence when a short circuit is detected.
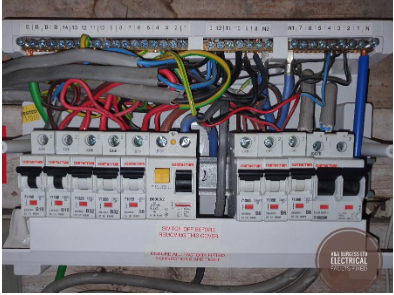
Circuit breakers will trip in one of two ways:
Overload - When too many electrical appliances are used and the circuit breakers maximum operating current is exceeded. The circuit breaker contains a bi-metallic strip that makes the contact inside. As the circuit is used under normal conditions, this bi-metallic strip warms up and continues to make contact. As the level of electrical current increases with demand and exceeds the preset level inside the breaker, the strip, being made of two different metals, begins to bend and eventually breaks contact inside the circuit breaker. When this occurs, the electrical current flow is stopped and the switch for the breaker trips.%20
Electrical Fault Conditions - When a short circuit occurs, a very large electrical current occurs and the circuit breaker needs to trip more quickly to prevent damage. In these circumstances, the solenoid inside will detect the large fault current and operate more quickly than the bi-metallic strip.
Back to top9) Electrical Repair and Maintenance
Addressing electrical repair needs promptly can lengthen the life of the overall wiring system. If you suspect a short circuit or other electrical issues, do not attempt DIY fixes; instead, seek professional electrical services. Qualified electricians can troubleshoot electrical faults, repair loose wire connections, replace damaged wires, and ensure your home is safe from potential electrical hazards.%20
A good way of ensuring that your home is adequately protected is to have regular electrical checks carried out. As an electrician and teacher, I am often asked how often electrical systems should be checked to ensure safe operation and the answer depends upon the installation and use.%20
Domestic homes should be checked after they reach ten years of age and again every ten years. Where there are signs of deterioration in the electrical system it may be necessary to increase the frequency of electrical testing to monitor the condition of the electrical wires, equipment and system condition.
Back to top10) Summary
Understanding what an electrical short circuit is and the most common causes of short circuits can help homeowners take the necessary steps to prevent considerable damage and ensure electrical safety. Regular maintenance, safety measures, and awareness of the signs of damage will help in keeping your property safe from the dangers of short circuits and other electrical issues. Always consult a licensed electrician for electrical inspections, repairs, and installations to maintain a safe electrical system.
By being proactive and attentive to the signs of potential electrical faults, you can protect your home, your loved ones, and your property from the dangers of electric short circuits.
%20
- Inicie sesión para enviar comentarios