What causes Electrical Arcing. Why Electricity Arcs - Electrical Faults Fixed
Table of Contents
- What Causes Electrical Arcing: Why Electricity Arcs
- The Physics of Electrical Arcing
- Common Causes of Electrical Arcing
- Types of Electrical Arcing
- The Dangers of Electrical Arcing
- Preventing Electrical Arcing
- Detecting and Responding to Electrical Arcing
- If you suspect electrical arcing:
- Electrical Arcing in Different Settings
- Advanced Technologies in Arc Prevention and Mitigation
- The Future of Electrical Safety
- Conclusion
1) What Causes Electrical Arcing: Why Electricity Arcs
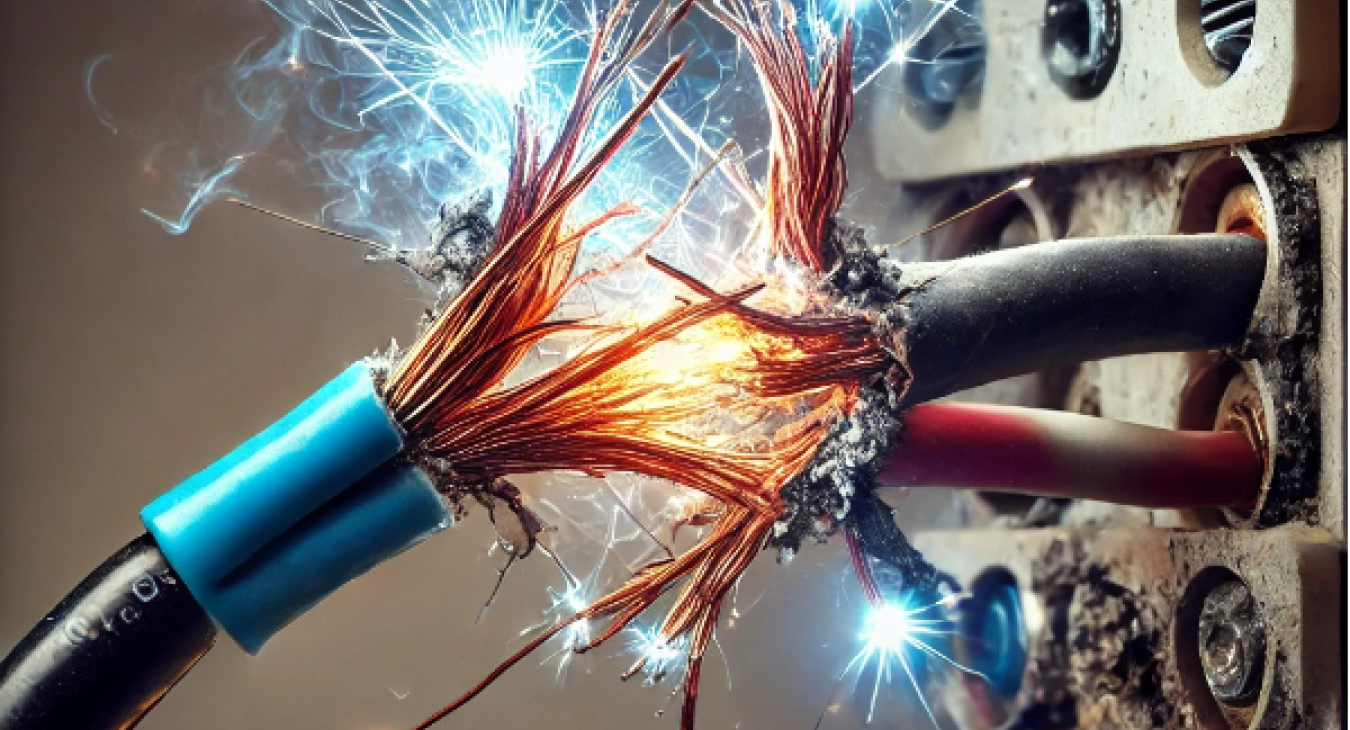
Electrical arcing is a phenomenon that occurs in electrical systems when an electric current flows through an air gap between two conductors. This process can lead to potential hazards, including electrical fires, equipment damage, and severe injuries. Maintaining safe electrical equipment and preventing accidents in both residential and industrial settings is vital to prevent issues like electrical arcing.
In my career as an emergency electrician, I am regularly called to electrical systems that have been arcing and will advise customers of the best ways to avoid such electrical problems.
Back to top2) The Physics of Electrical Arcing
Electrical arcing, also known as arc flash or electric arcing, happens when electricity jumps across an open space in an electrical circuit. This phenomenon occurs due to the ionization of air molecules, creating a conductive path for the electrical current. The result is a visible bright flash of light and intense heat, often accompanied by a loud noise and a pressure wave.
The occurrence is common in higher powered electrical circuits and can often be heard behind plug sockets. If your plug sockets are crackling then it is likely that electrical arcing is occurring.
The temperature at the point of the arc can reach high temperatures comparable to the surface of the sun, sometimes exceeding 35,000 degrees Fahrenheit. This extreme heat can cause severe burns, melt metals, and ignite nearby combustible materials, making electrical arcing a major problem in terms of safety and equipment integrity.
The heat of an electrical arc does depend on various factors such as circuit impedance and voltage levels. Arcing is one of the common causes of a burnt plug socket.
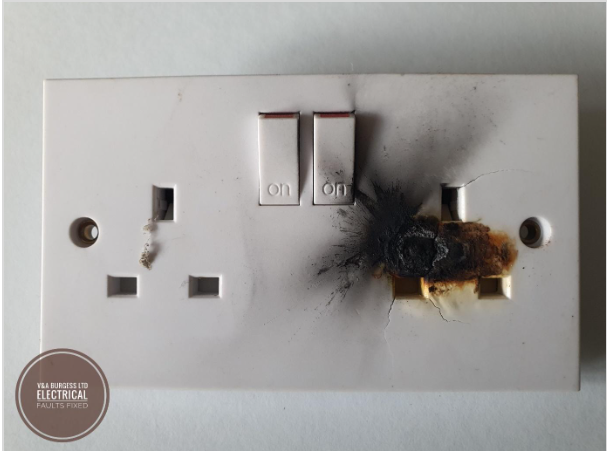

3) Common Causes of Electrical Arcing
Several factors can contribute to the occurrence of electrical arcing. Understanding these common causes is essential for implementing effective preventative measures. Here are some of the primary reasons why electricity arcs:
- Loose Connections: When electrical connections loosen, they can create gaps that allow electricity to jump, resulting in arcing. This is often seen in electrical outlets, power points, and electrical switches. Effects are amplified in higher powered electrical circuits.
- Damaged Insulation: Damaged wire insulation can expose conductors, creating opportunities for arcs to form between the wire and nearby conductive surfaces.
- Short Circuit: A short circuit occurs when there's an unintended path for electrical current to flow. This can lead to arcing as the electricity tries to find the path of least resistance.
- Overloaded Circuits: Excessive current flowing through a circuit can cause overheating, potentially damaging insulation and leading to arcing.
- Environmental Factors: Dust, moisture, and corrosive atmospheres can degrade electrical components, increasing the likelihood of arcing.
- Equipment Failure: Wear and tear on electrical equipment can lead to component failure and subsequent arcing.
4) Types of Electrical Arcing
Electrical arcing can be categorized into different types, each with its own characteristics and potential dangers:
- Series Arc: This occurs when there's a break in a single conductor, such as a damaged wire or a loose connection in a series circuit.
- Parallel Arc: This happens when there's unwanted current flow between two separate conductors, often due to damaged insulation.
- Ground Arc: This type of arc occurs when there's an unintended current path between a conductor and a grounded surface.
- Arc Flash: An arc flash is a type of electrical explosion that can occur in high voltage systems, resulting in a dangerous release of energy.
5) The Dangers of Electrical Arcing
Electrical arcing poses numerous risks to both people and property:
Electrical Fires: The intense heat generated by arcing can easily ignite surrounding materials, leading to devastating fires

- Severe Burns: Direct exposure to an electrical arc can cause severe, life-threatening burns due to the extremely high temperatures involved.
- Arc Blast: The explosive force of an arc blast can throw individuals across a room, causing serious injuries.
- Hearing Damage: The loud noise associated with arcing can cause immediate or long-term hearing damage.
- Equipment Damage: Arcing can cause extensive damage to electrical equipment, leading to costly repairs or replacements.
- Toxic Fumes: The high temperatures of an arc can vaporize metals and other materials, creating toxic fumes.
6) Preventing Electrical Arcing
Preventing electrical arcing is crucial for maintaining safe electrical systems. Here are some key preventative measures:
- Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine inspections and maintenance of electrical equipment to identify and address potential issues before they lead to arcing.
- Proper Installation: Ensure that all electrical work is performed by a qualified electrician who follows the National Electrical Code and local regulations.
- Use of AFCIs: Install Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) in electrical panels. These devices can detect and interrupt arcing faults before they become dangerous.
Avoid Overloading Circuits: Don't exceed the rated capacity of circuits, and be cautious when using extension cords or multiple high-power devices on a single circuit.
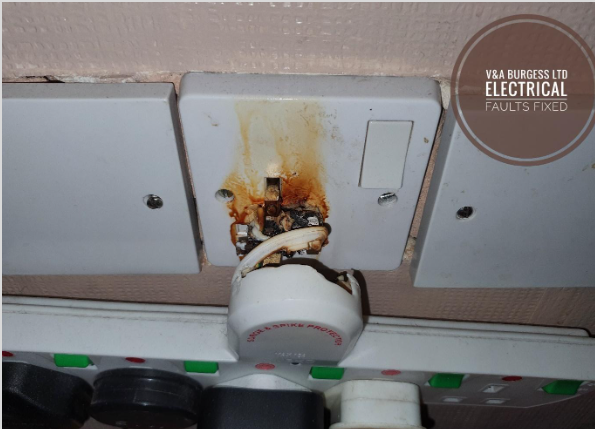

- Proper Equipment Selection: Use electrical equipment rated for the specific application and environment.
- Education and Training: Provide proper training for individuals working with or around electrical systems to reduce the risk of human error.
- Implement Safety Standards: Follow industry safety standards, such as those set by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), particularly in industrial settings.
- Use of PPE: When working on or near energized equipment, use appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) to protect against arc flash hazards.
7) Detecting and Responding to Electrical Arcing
Recognizing the signs of electrical arcing can help prevent serious damage and danger:
- Unusual Sounds: Listen for buzzing, hissing, or popping sounds from electrical outlets or equipment.
- Visual Cues: Look for spark plugs-like flashes, smoke, or charring around electrical connections.
- Odors: Be alert to burning smells, which may indicate overheating or arcing.
- Flickering Lights: Unexplained flickering of lights, especially in fluorescent lighting, can be a sign of arcing.
8) If you suspect electrical arcing:
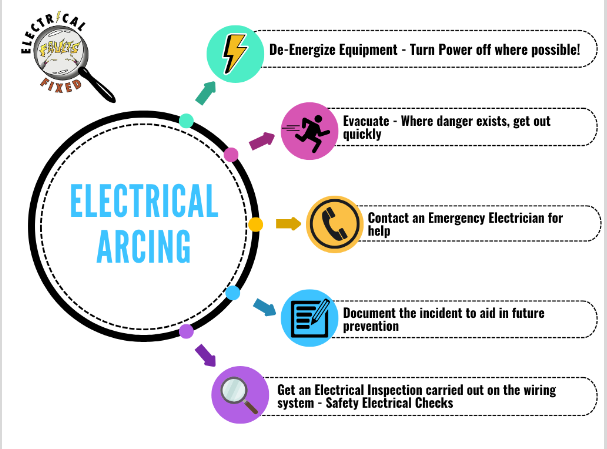
9) Electrical Arcing in Different Settings
The risk and nature of electrical arcing can vary depending on the setting:
- Residential: In homes, especially older homes, common areas of concern include electrical outlets, light switches, and electrical panels. Arc fault circuit interrupters are now required in many areas of new construction, including bedrooms, family rooms, and dining rooms.
- Industrial: Industrial settings often involve high voltage systems and heavy-duty equipment, increasing the risk of severe arc flash events. Arc welding is a controlled form of arcing used in manufacturing.
- Commercial: Office buildings and retail spaces may face risks from overloaded circuits, aging infrastructure, and high-use equipment like power points and fluorescent lighting.
- Outdoor: Electrical arcing can occur in outdoor settings due to environmental factors like moisture, wildlife interference, or storm damage to power lines.
10) Advanced Technologies in Arc Prevention and Mitigation
As awareness of the dangers of electrical arcing has grown, so too have the technologies designed to prevent and mitigate these risks:
- Advanced AFCIs: Modern Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters use sophisticated algorithms to differentiate between normal arcing (like in motors or arc welders) and dangerous arcing faults. (In the UK AFCI are known as AFDD (Arc Fault Detection Devices))
- Arc Flash Relays: These devices can detect the light from an arc flash and trigger protective measures in milliseconds.
- High-Speed Cameras: Used in field tests and research to capture and analyze arc flash events in slow motion.
- Infrared Thermography: Regular scans can identify hot spots in electrical equipment that may indicate potential arcing risks.
- Partial Discharge Testing: This non-destructive test can detect insulation degradation before it leads to arcing.
- Automatic Fire Suppression Systems: Specialized systems designed to quickly extinguish electrical fires caused by arcing.
11) The Future of Electrical Safety
As technology advances, we can expect to see continued improvements in electrical safety:
- Smart Electrical Systems: Integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology to monitor and predict potential arcing risks in real-time.
- Advanced Materials: Development of new insulation materials and coatings that are more resistant to arcing and degradation.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered systems that can predict and prevent electrical faults before they occur.
- Improved Standards: Ongoing updates to safety standards like the National Electrical Code and BS7671 (UK) to address new technologies and known risks.
12) Conclusion
Electrical arcing remains a significant concern in electrical systems across the United States and worldwide. Understanding its causes, recognizing its signs, and implementing proper safety measures are crucial steps in preventing the potential dangers associated with this phenomenon.
From the use of arc fault circuit interrupters in our homes to the implementation of comprehensive arc flash hazard assessments in industrial settings, a multi-faceted approach is necessary to mitigate the risks of electrical arcing. Regular maintenance, proper training, and adherence to safety standards play vital roles in preventing arc flash incidents.
Remember, when it comes to electrical safety, there's no substitute for professional expertise. If you suspect any electrical issues in your home or workplace, don't hesitate to consult a qualified electrician. Your safety and the integrity of your electrical systems depend on it.
Back to top
Read more articles
- Log in to post comments


